HDMA design, preparation, and application has incorporate a proton acceptor in the carbocation skeleton, generating a novel immonium salts.
HDMA is a peptide coupling agent with increased coupling efficiency and lower racemization compared to HATU.
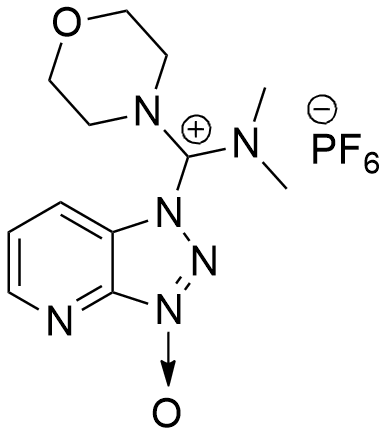
CAS: 958029-37-3
Synonym: 1-[(Dimethylamino)(morpholino)methylene]-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyridine-1-ium 3-oxidehexafluorophosphate
Properties
Purity
≥99.0%
Molecular Formula
C12H17F6N6O2P
Molecular Weight
422.3 gr/mol
Appearance
White to off-white crystalline powder
Storage Conditions
store in a cool and dry place (2-8oC)
Applications
- HDMA present enhanced solubility (due to of the oxygen atom in the carbon skeleton), which is the first property to be taken into account, having it’s great influence on the reaction yield and its performance in the automatic synthesizers. This enhanced solubility should help the removal during the workup after the coupling of the urea formed in a solution mode approach.
- Couplings involving immonium salts, such as HDMA are carried out with an excess of base, at least 2 equiv.. In this regard, coupling reactions carried out with HDAMA allowing the use of just 1 equiv. of base. This fact has great importance on the economical savings in the production of bulk quantities of peptides.
Studies
- Novel Proton Acceptor Immonium-Type Coupling Reagents: Application in Solution and Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis
A. El-Faham and F. Albericio Org. Lett., 2007, 9 (22), pp 4475–4477.
Read Article